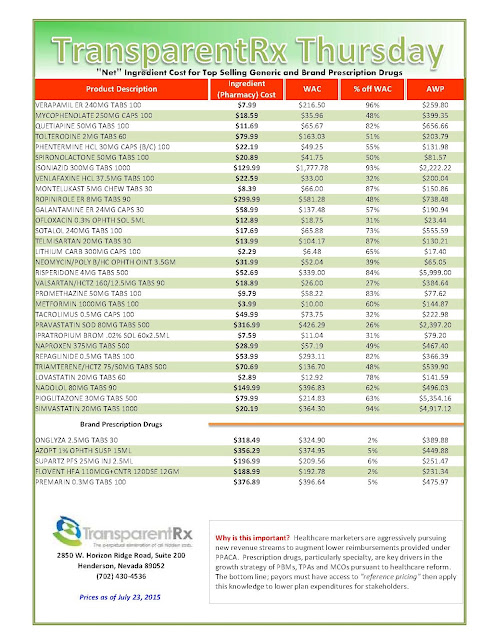
Most employers have been using multi-tier prescription drug plans for many years, but new data released from the 2014 UBA Health Plan Survey shows a significant increase in the use of 4-tier plans, which typically cover the highest cost drugs, as well as major increases in corresponding median copays — a trend that is expected to continue, according to UBA.
UBA’s survey finds that, since 2009, the number of 4-tier plans has grown from 13.6 percent to 32.9 percent of all plans offered, a 141.9 percent increase. Since 2012, tier 4 median copays have also grown 25 percent; in 2014, 4-tier plans had median copays of $10, $35, $55 and $100.
“There may be future shifts in these copays since prescription copays and deductibles must track to out-of-pocket maximums under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA),” says Mark Bagnall, CEO of BAGNALL. “However, general competitive pressure will demand that employees contribute more for the highest tiers.”
UBA expects that specialty drug costs will continue to drive the maximum possible copay increases in this tier. “Not only must copays cover the rising costs of these drugs driven by the pharmaceutical industry but they must cover the merging physician commissions given for some specialty drugs,” says Mike Mulqueeney, VP, Johnson & Dugan Insurance Services Corporation.
“We’re already seeing some employers using a 6- or even 7-tier drug plan,” says Carol Taylor, Employee Benefit Advisor, D & S Agency. “When you have an employee taking a drug that costs $30,000 a month, a $100 copay is not sustainable. Eventually, we’ll reach a point where the insurers won’t be able to recoup the cost of prescription drug cost increases. Because of the out-of-pocket maximums in place by the ACA, the only way to offset the increased prescription drug costs will be through higher premium increases.”
According to UBA’s survey, 57.1 percent of all prescription drug plans utilize three tiers (generic, formulary brand, and non-formulary brand), 6.8 percent retain a 2-tier plan, and 32.9 percent offer four tiers or more. In five years (since 2009), the number of 3-tier plans has decreased 20.4 percent (from 71.7 percent to 57.1 percent) and 2-tier plans have decreased 45.6 percent (from 12.5 percent to 6.8 percent) in that same time period.
PRESCRIPTION DRUG PLAN TIER PREVALENCE BY EMPLOYER SIZE
- Employer size with the most 3-tier plans: employers with 500 to 999 employees (70%)
- Employer size with the least 3-tier plans: employers with fewer than 10 employees (48.2%)
- Employer size with the most 4-tier plans: employers with 10 to 24 employees (40%)
- Employer size with the least 4-tier plans: employers with 500 to 999 employees (20%)
“Employers with 500 to 999 employees haven’t had to go with 4-tier plans yet. These groups are truly experience rated and need to keep a constant eye on their loss ratio. Because prescription costs are increasing at a very rapid pace, and new, much more expensive, drugs are coming to the market they will be forced to look at adding a fourth and maybe even a fifth tier,” says Vicki Ferentz, Vice President, Acadia Benefits, Inc.
COPAY DESIGN
A majority (67.8 percent) of prescription drug plans utilize copays. Many used to offer copay only; in the last five years, however, most plans required the patient to pay coinsurance after the copay. UBA’s survey shows that, since 2010, the number of 2-tier plans with a prescription copay only (no coinsurance) decreased 42.9 percent, and the number of 3-tier plans with a copay only decreased 20.6 percent.
Read more: http://www.benzinga.com/pressreleases/15/07/p5708454/employers-use-of-multi-tier-pharmacy-benefits-continues-to-rise#ixzz3hI7z2tkt
 Most employers have been using multi-tier prescription drug plans for many years, but new data released from the 2014 UBA Health Plan Survey shows a significant increase in the use of 4-tier plans, which typically cover the highest cost drugs, as well as major increases in corresponding median copays — a trend that is expected to continue, according to UBA.
Most employers have been using multi-tier prescription drug plans for many years, but new data released from the 2014 UBA Health Plan Survey shows a significant increase in the use of 4-tier plans, which typically cover the highest cost drugs, as well as major increases in corresponding median copays — a trend that is expected to continue, according to UBA.