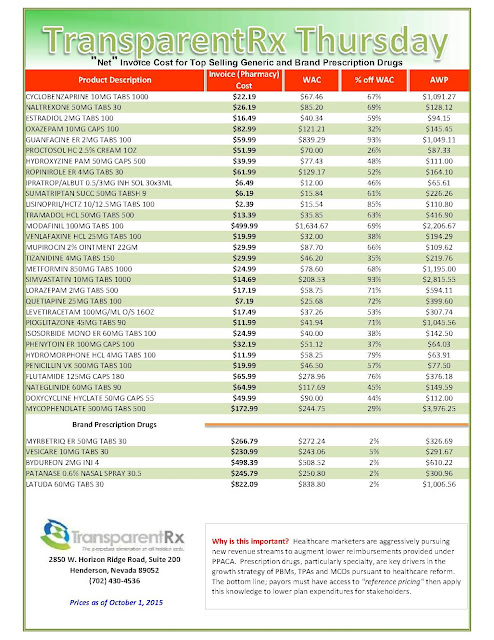
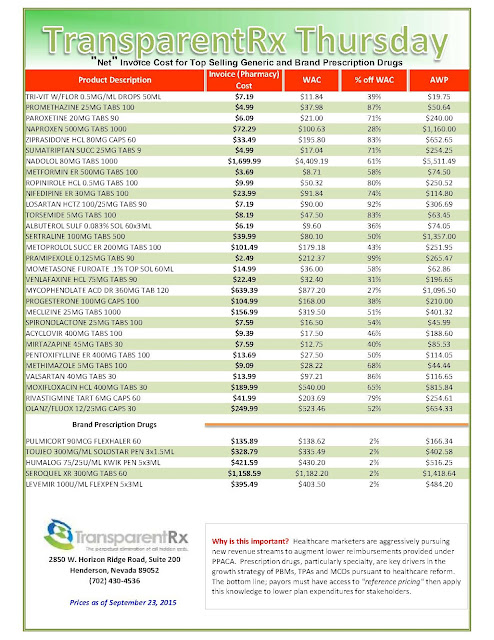
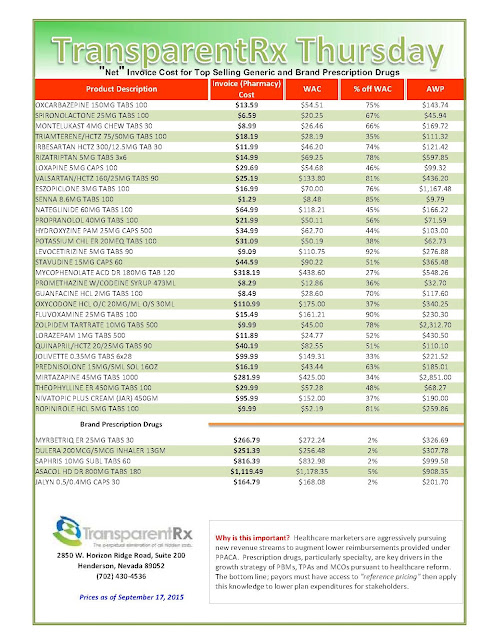
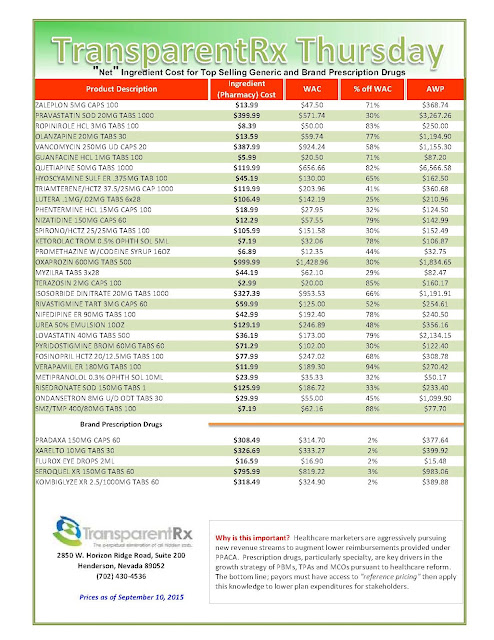
|
| [Click to Enlarge] |
The pharmacy benefit management industry is experiencing subtle changes, and a leadership shuffle at the country’s largest PBM has experts speculating about whether PBMs will remain stand-alone companies.
More healthcare organizations view prescription drug use as a critical element of keeping patients healthy and reducing costs, and controlling a PBM could help with a population health strategy. “You could see a pathway forward where the PBMs become more integrated with the payers,” said Jon Kaplan, managing director at Boston Consulting Group.
PBMs handle prescription drug benefits for employers and health insurers, a role that includes negotiating drug discounts with pharmaceutical companies, building pharmacy networks and creating their own drug benefit plans. They usually play second fiddle to the insurance companies that handle medical benefits, but PBMs have become more relevant in recent years due to the rising prices of brand-name and generic drugs.
Skyrocketing prescription drug spending was a major reason the growth rate of the nation’s healthcare tab increased from historical lows in 2014. Consequently, drugs have become a bigger political issue. Presidential hopeful and Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.) has proposed numerous bills over the past few years to control drug prices. Democratic presidential candidate Hillary Clinton outlined her own prescription drug reforms this week. Her plan came out right after the CEO of Turing Pharmaceuticals, a startup drug company, inflated the price of one of its drugs by more than 5,400%—a move that drew widespread ire from the public.
Express Scripts Holding Co. is the largest PBM in the country with about $100 billion in annual revenue. The St. Louis-based company has been notably outspoken about the high sticker prices of new specialty drugs that have hit the market recently, such as the hepatitis C drugs Sovaldi and Harvoni that are manufactured by Gilead Sciences. High-cost drugs have been eating into the profits of PBMs.
Paz retirement seen as foreshadowing a deal
Earlier this month, Express Scripts announced CEO George Paz will retire from his position next spring. President Tim Wentworth will take over. Although it was a somewhat routine executive move, many analysts covering the industry viewed the switch at Express Scripts as a possible step toward a sale or merger.
“We are positive it was announced sooner rather than later as it allows new management to better address challenges that lie ahead,” Charles Rhyee, a managing director at Wall Street firm Cowen & Co., said about Express Scripts in a research note this month.
One of those challenges involves Express Scripts’ contract with health insurer Anthem. Anthem has publicly said it is looking to renegotiate the contract, which expires in 2019, and expects to save between $500 million and $700 million with new terms. Anthem has some leverage because it is buying Cigna Corp. in a deal valued at more than $54 billion. Cigna uses Catamaran Corp. as its PBM, and Anthem could switch to that vendor.
Anthem could also bring drug benefit management functions in-house. “All options are open,” Anthem CEO Joseph Swedish said at a Morgan Stanley conference this month about the company’s PBM situation.
Paz and Wentworth were not available for an interview. But an Express Scripts spokesperson released a broad statement saying, “We’re focused on practicing pharmacy smarter—putting medicine within reach by being uniquely aligned with clients, and taking bold actions to make prescription drugs more affordable and accessible. Our business model of alignment resonates with our clients more than ever, our specialized care model delivers better patient outcomes, and our size and scale position us well for success in any environment.”
But industry observers say stand-alone PBMs like Express Scripts face an uphill financial battle. Aside from dealing with high drug prices, many companies have used most of the weapons in their arsenal to keep drug costs down. For instance, the national generic drug usage rate is around 78% and rising. “Most levers that the PBMs could press have been pressed,” Kaplan said.
Sundar Subramanian, a healthcare partner at Strategy&, the consulting arm of PricewaterhouseCoopers, said PBMs fall into two groups. The first is the traditional scale model, where a PBM focuses on filling as many prescriptions as possible and driving down drug costs through use of generics, tiered formularies and mail orders. Express Scripts invested heavily in this model in 2012, when it bought competitor Medco Health Solutions for $29 billion. The more popular model is a strategic one, he said. It involves companies that aren’t traditional PBMs that want to better integrate medical and drug benefits.
A quick path to value-based payments
Insurers and pharmacies see PBMs as a way to advance more quickly to value-based payments, and they can use their claims and data analytics to find out, for example, which patients need more help in adhering to their drug regimens. “You can understand specific ways to engage with those members and keep them out of hospitals,” Subramanian said. “Those kinds of opportunities never come about just from the PBM side.”
Some integration has already taken shape. CVS Health Corp. made one of the first big moves almost a decade ago when it bought Caremark Rx. UnitedHealth Group bought Catamaran for $12.8 billion this year and is fusing the company into its OptumRx subsidiary. Pharmacy chain Rite Aid acquired EnvisionRx for $2 billion in February. Aetna, which is in the process of acquiring Humana, has expressed interest in creating its own Optum-like health services unit. Humana’s internal PBM would be a major part of it.
The dealmaking has isolated Express Scripts, analysts say. “Express Scripts does not have the retail pharmacy nor the captive growth engine,” said Ana Gupte, managing director at investment bank Leerink Partners. “It’s very possible they could merge with a retail pharmacy, or they get bought by a managed-care organization.”
Rhyee speculated that Express Scripts could be a prime target for Walgreens Boots Alliance, the parent company of the national chain of Walgreens retail pharmacies. Walgreens lacks a drug benefit component after it sold its PBM a few years ago, and adding Express Scripts would immediately rival CVS, “which has been gaining share” over Walgreens, Rhyee said. Walgreens did not respond to a request for comment.
Not all healthcare groups are fans of PBM consolidation, or even PBMs in general. The National Community Pharmacists Association says PBMs often squeeze local community pharmacies with “take-it-or-leave-it” contracts even though independent pharmacists play critical roles in advancing population health in communities.
Written by Bob Herman