A young husband was diagnosed with advanced melanoma and tumors attached to his brain. Waiting on the other side of his oncology clinic’s pharmacy counter was a potentially life-prolonging drug. But his Pharmacy Benefit Manager pumped the brakes, instead requiring that he and his wife order the medication from the mail-order pharmacy owned by that PBM — and submit a $1,000 co-pay.
By the time his wife was able to procure co-pay assistance, the young man could no longer swallow pills and passed away in the ICU. Medication that was critical to treating his cancer remained just on the other side of the clinic’s pharmacy counter, with access denied by the couple’s PBM.
It’s a heartbreaking story. Patients should never be delayed or denied access to needed care. But such instances are becoming more common because of large PBMs — powerful middlemen that manage health care benefits for more than 260 million Americans. PBMs decide what drugs are covered by insurance, how much they should cost, and how they get into patients’ hands.
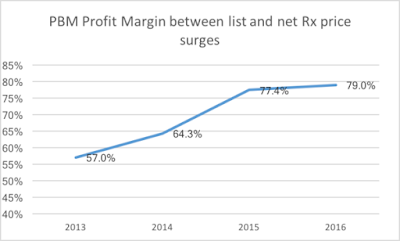
PBMs use their outsized power to reap tremendous profits, particularly through a variety of different fees with different names known broadly in the industry as “Direct and Indirect Remuneration” or “DIR” fees. DIR fees are charged to pharmacies months after a patient buys a prescription.
Ostensibly in place to incentivize pharmacy performance, DIR fees only serve to increase PBM profits. In fact, they have no basis in regulation or law and are just part of an already convoluted system that PBMs have rigged to boost their bottom line at the expense of patients.
What is particularly galling is that the DIR fees PBMs charge pharmacies are ultimately paid for by our most vulnerable patients — the sick and the elderly on Medicare. What happens is that:
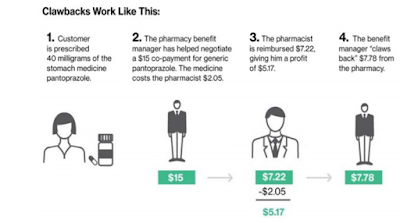
- a patient buys a drug based on an inflated price that includes DIR Fees at a pharmacy;
- the PBM is reimbursed by Medicare for the original, lower price of the drug;
- months later, the PBM gets paid again after demanding a DIR fee from the pharmacy that sold the drug, “clawing back” up to 11 percent of what the pharmacy charged.
Shouldn’t those savings on pricey cancer drugs have been reimbursed to the patient or never passed on in the first place?
Meanwhile, the inflated price of the drug is counted against the patient on Medicare — helping to push them straight into the “donut hole,” where they are responsible for 100 percent of prescription costs. It’s hard to believe, but this deliberate fleecing of Medicare patients is completely legal.
And this is just one of the many ways PBMs manipulate the health care system to pad their own pockets, drive neighborhood pharmacy competitors out of business, and contribute to a toxic culture that puts profits over patients.
For Americans battling cancer, PBMs and the barriers to quality, affordable, and accessible care they present are particularly horrifying. Most of the 1.5 million diagnosed with cancer each year will obtain the lifesaving treatment they need in the community practice setting. That’s why it is so vital to keep this cancer care in community settings, rather than the PBMs practice of diverting patients from the support they need to beat this devastating disease.
Today, many oncology clinics have specialty pharmacies on site with staff that goes above and beyond for patients — providing counseling on taking these powerful medications with potentially dangerous side-effects, lining up financial assistance, and ensuring the medications get to patients quickly.
After this hard work, PBMs often swoop in and demand that a cancer patient switch to the PBM-owned mail-order pharmacy, which can result in unnecessary and dangerous delays. You already know why: There’s money in it.
PBMs are multi-billion dollar corporations with a powerful lobby in Washington, D.C. With legislation pending to address PBM abuses practices such as DIR fees, we can’t let lawmakers forget the stakes. Congress needs to take action now to stop PBM abuses before it’s too late for another patient in need.
by Jeff Vacirca, MD
Dr. Vacirca is the CEO of New York Cancer Specialists and president of the Community Oncology Alliance