Tuesday Tip of the Week: You Should Not Pay a PBM for Your Own Claims Data
The competitive advantage represented by industry know-how, trade secrets, or unique benefit designs is translatable directly into profits. Non-fiduciary PBMs go to great lengths to protect whatever competitive advantage is attained.
In PBM contracting, competitive advantage can easily evolve into misaligned incentives. PBM autonomy of critical claims data, manufacturer rebates, or benefit design procedures can eliminate effective performance measurement. Here is an example of a trap you don’t want to find yourself in.
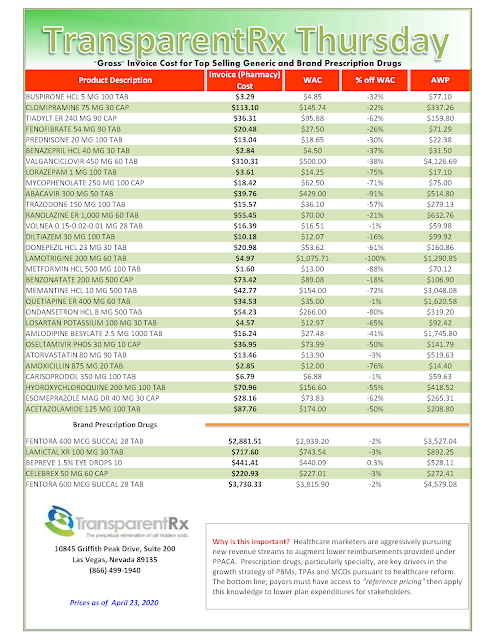
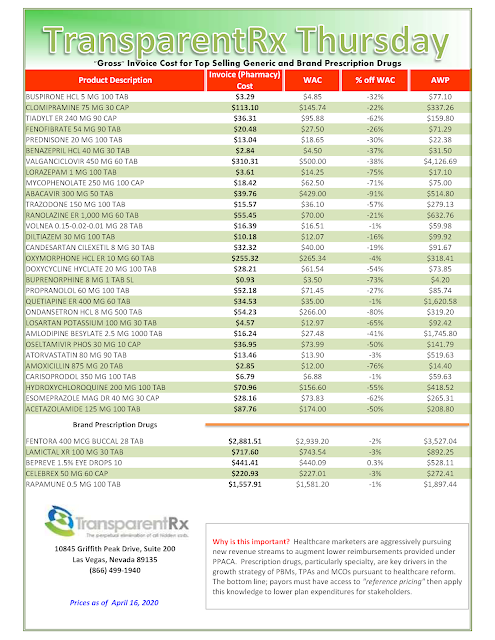
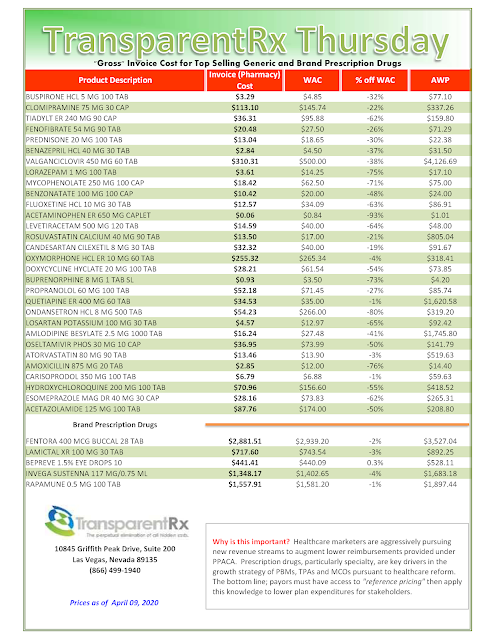
 |
| CLICK TO ENLARGE |
The balancing of a plan sponsor’s rights in accessing valuable claims information and know-how and the PBM’s need to hide cash flows is dictacted, in large part, by the pharmacy services agreement. The contract nomenclature, and the clauses it prescribes, must provide a mechanism by which a proper balance between radical transparency and reasonable profits to the PBM may be struck.
Plan sponsors should not have to pay for their own data. If a PBM suggests it is their policy, it is a money grab nothing more. That cost and service should be built into their administartive fee. Oh wait, did you agree to the $0 admin fee and $0 dispensing fee? If yes, then this is the price you might pay in exchange for the artifically low administrative fees.
A radically transparent or fiduciary-model PBM makes money just one way – the administrative fee. When the administrative fee is artificially low (less than $4 per claim) the likelihood of your PBM being radically transparent is slim to none. In some form, it is generating huge overpayments or mark ups via hidden cash flow.