Biosimilars are an emerging area in the specialty pharmacy community and beyond. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to feel outside pressure from costly drugs, strategies to reduce health care spend are being sought.
Although biologics account for less than 1% of all dispensed prescription drugs in the United States, it accounts for one-fourth of all prescription spending. Concern surrounding high price tags of biologics continues to rise, and biosimilars offer the potential to provide patients with less costly alternatives.
 |
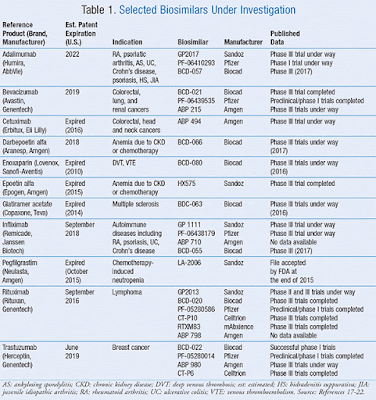
| Table1: some of the trials being conducted on biosimilars |
In an interview with Specialty Pharmacy Times, Yogesh Soneji, a partner at Trinity Partners, discusses the future of pharmacy and the effect of biosimilar approvals.
SPT: What impact can biosimilar approvals have on the pharmaceutical marketplace?
Soneji: I think these are exciting times. It’s almost a new era for the industry in general, [with] the launch of recent biosimilars and some uncertainty around what happens in the near term. TABLE 1 lists some of the trials being conducted on biosimilars, and if successfully completed, these products may become available in the near future.
When you think about the marketplace there are so many different players. A way I think about this is there are going to be 2 camps: the brand to whom a biosimilar is being launched against and then the biosimilars themselves. The impact is going to be different depending on what side of the fence you are on.
For the branded companies that have biologics today, it’s going to be a little more uncertain in the near term of what happens, because besides the upcoming launch timing of biosimilars, they also have to have to guess what the pricing (of biosimilars) is going to be, what the biosimilars will discount their drugs at, and there is going to be some uncertainty, at least in the near term, on how to mitigate that. On the other hand, for the companies that are actually launching these biosimilars, that represents a whole world of opportunities.
SPT: How will biosimilars affect future drug prices?
Soneji: Only time will tell, but if you even see what is going on recently, you have biologics with different price points, with one in the 15% discount list price and another over 30% discounted list price. I think it’s already been mentioned that the branded players, like Remicade, have been more aggressive on contracting on their own drug and getting better contracting in order to safeguard their business in the near term. I think there is no doubt that we will see prices go down and spiral, but the question isn’t about whether they will or not. I think the question is how fast and what that path looks like. If it’s going to happen very quickly or if it’s going to happen in a steadier manner over time.
I do think in the long run, biosimilars will drive down prices. One key aspect with pricing that’s a little more complicated in the drug industry, as you might have seen, is it is not very transparent about what the price of the drug is.
We see list prices mentioned regularly in press releases about Inflectra and what their list price is compared to the list price of Remicade. But I think the key here is for us to keep an eye out for not just the list price, but what is the net price, which takes into account the rebates and discounts which can be negotiated on a payer basis, and what happens to those and what path those take. Because that is what drives decisions, especially from the payer side. Which drugs they put on formulary, which drugs they prefer to use at the end of the day, what really matters with pricing is net price that payers have to pay including contracts/rebates and discounts.
Read more >>