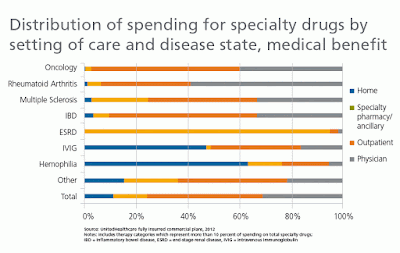
Express Scripts Holding Co., a large manager of prescription-drug benefits for U.S. employers and insurers, is seeking deals with pharmaceutical companies that would set pricing for some cancer drugs based on how well they work.
My Comment: This is good for payors and long overdue. In February I published, “Specialty Pharmacy: The Top 10 Trends Payers Should Be Following” which listed pay-for-performance as the # 1 trend to follow.
The effort is part of a growing push for so-called pay-for-performance deals amid complaints about the rising price of medications, some of which cost more than $100,000 per patient a year.
Some insurers and prescription-benefit managers are pushing back by arguing that they should pay less when drugs don’t work well in certain patients. Drug companies are countering with pricing models of their own, such as offering free doses during a trial period.
 Express Scripts this month told clients it is seeking deals with drug makers for differentiated pricing for certain cancer drugs based on how well they work against different types of tumors, Express Scripts Chief Medical Officer Steve Miller said in an interview. Currently, Express Scripts and most insurers pay the same per-unit rate for a cancer drug regardless of the type of cancer it is being used to treat.
Express Scripts this month told clients it is seeking deals with drug makers for differentiated pricing for certain cancer drugs based on how well they work against different types of tumors, Express Scripts Chief Medical Officer Steve Miller said in an interview. Currently, Express Scripts and most insurers pay the same per-unit rate for a cancer drug regardless of the type of cancer it is being used to treat.
Dr. Miller pointed to Tarceva, a drug co-marketed by Roche Holding AG and Astellas Pharma Inc., which has shown a smaller benefit in pancreatic cancer than in lung cancer. In one clinical trial, Tarceva extended the median survival of pancreatic cancer patients by less than two weeks versus placebo. In a separate trial, it prolonged survival among lung cancer patients by about 3 ½ months versus chemotherapy.
In an “indication-specific pricing” model, the per-pill cost of Tarceva would be lower for pancreatic-cancer patients than for lung-cancer patients, given the reduced efficacy, Dr. Miller said. Tarceva currently costs about $6,850 a month per patient, according to GoodRx, a website that tracks drug prices.
“One of the big frustrations has always been people paying top dollar for drugs that aren’t always giving them the best response,” Dr. Miller said. “If pharma is truly sincere about wanting value-based reimbursement, we now have the sophistication to do that.”
Although Dr. Miller used Tarceva as an example, he wouldn’t identify the drugs for which Express Scripts is seeking indication-specific pricing. The company has begun approaching drug makers about arranging such deals, which could go into effect for 2016, he said.
My Comment: How much of the savings are going to be passed back to clients? Those self-funded payors which assume 100% pass back are incorrect unless they have a fiduciary contract. PBMs are rewarded when they’ve won your business and not for doing their job lest you’ve established some very specific performance bonuses.
A spokeswoman for Roche’s Genentech unit said that when Tarceva was approved to treat pancreatic cancer in 2005, it was the first medicine approved for the disease in more than a decade. She said the drug is now rarely used to treat pancreatic cancer because other drugs have since been approved for the disease. She said Genentech would welcome a system of pricing a medicine based on how it performs in different indications—and has one in place in Italy—but there are challenges to doing so in the U.S., including fragmented patient-record systems.
Express Scripts has in recent years been a vocal critic of high drug prices, which the company has used to promote its services to potential customers as it competes against CVS Health Corp. and others to administer drug benefits for health insurers and large employers. Pharmacy-benefit managers also sometimes keep a portion of the rebates and discounts they negotiate from pharmaceutical companies.
Express Scripts’ approach would be similar to that proposed by Peter Bach, director of the Center for Health Policy and Outcomes at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
In an article published last year in the Journal of the American Medical Association, he suggested that in an indication-specific arrangement, the monthly price for Eli Lilly & Co.’s cancer drug Erbitux would plummet from $10,320 a patient to about $470 a patient for its least effective use, treating recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer. The drug also is used to treat locally advanced head and neck cancer, as well as colorectal cancer.
A Lilly spokeswoman said Lilly supports efforts to make cancer drug reimbursement “better reflect treatment value for different patient populations,” and it is “exploring alternative options to accurately represent the value our medicines offer across multiple indications.”
Drug pricing has been “very hard for the payers to do anything about,” said Steven Pearson, president of the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, a Boston nonprofit that evaluates cost-effectiveness in medicine. “Now they’re starting to think very hard about it, to look for practical ways to have more of an influence on pricing.”
It can be difficult for drug companies and payers to agree on terms of alternative payment deals—and to actually administer the deals.
To read more click here.







_1.jpg)

_1.jpg)