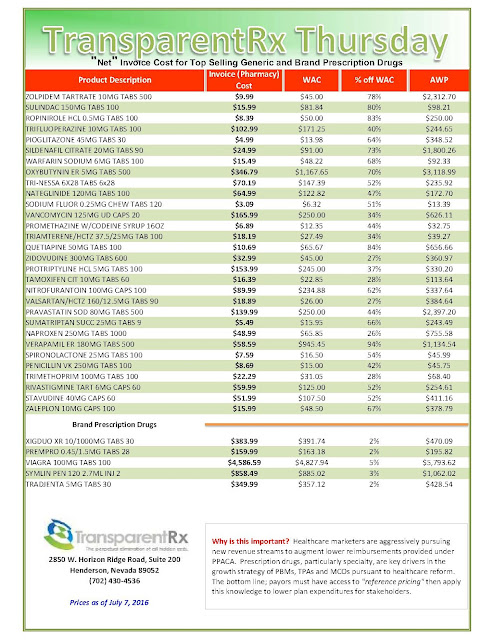
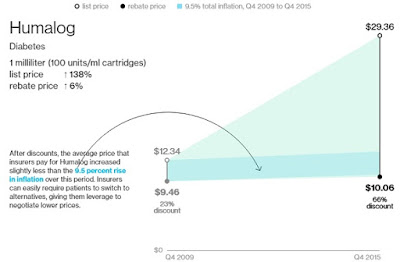
A McCandless pharmacist is calling attention to what he considers an unfair audit process, unseen by the public, where third-party pharmacy benefit managers contracted by commercial insurers use what some pharmacists consider questionable grounds to deny prescription payments.
 |
Mr. Adzema said the auditor pulled from his store, shown above, 19 prescriptions for medications costing
between $500 and $3,700, though he estimates 90 percent of his dispensed scripts cost less than $50. |
In this particular case, $55,402.47 worth of denials — to be withheld from future payments to the pharmacy.
————————-
Tyrone’s comment: This is a BIG, BIG deal. What happens to the dollars PBMs recover from pharmacies due to these audits? The dollars, sometimes huge amounts, are going into the bank accounts of traditional and pass-through PBMs when the money should in principle go back to plan sponsors who paid for the medications in the first damn place! I bet you [Benefits Directors, benefits consultants, principals etc…] haven’t had this conversation with your TPA or PBM. If not, shame on you. By the way, there is a name for this process and it’s referred to as back-billing. Though audits are necessary and sometimes produce good results, I am not a fan when the audit hurts stakeholders (i.e. patients, pharmacists and plan sponsors). The PBM is often the only beneficiary from this opaque process. The solution is to conduct your business with a fee-only or fiduciary TPA/PBM vendor.
————————-
Jay Adzema, pharmacist and owner of Adzema Pharmacy on Perry Highway, says an auditor for St. Louis-based Express Scripts — a leading pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) nationwide which administers plans for Highmark, UPMC Health Plan and others — came to his shop on June 29 after asking to review some of the 20,000 prescriptions he filled over the past two years.
Mr. Adzema said the auditor pulled 19 prescriptions for medications costing between $500 and $3,700, even though he estimates 90 percent of his dispensed scripts cost less than $50. He received the final 8-page audit report July 7, listing multiple errors from six cases for missing scripts, an incorrect supply for days needed, invalid or incomplete scripts or refills made too soon.
That experience illustrates a widespread tension that can pit auditors who see themselves as safeguarding the integrity and safety of dispensing medications against pharmacists who believe the audits can be largely a money grab that latch onto minor errors to deny claims.
Pharmacists’ complaints have grabbed the attention and support of some legislators as 33 states have passed laws regulating how PBMs conduct pharmacy audits.
Pennsylvania is not among them but Rep. Matthew Baker, R-Bradford County and chair of the House health committee, hopes to change that. Mr. Baker is prime sponsor of a bill, HB 946, which was recently passed by his House colleagues to address some of pharmacists’ concerns.
If the Senate approves and the bill is signed into law, Mr. Baker said the Pharmacy Audit Integrity Act law “establishes for the first time in Pennsylvania audit procedures, written report requirements, limitations, enforcement and will provide consistency and reliability for pharmacy audits.”
Insurers contract with pharmacy benefit managers to administer their prescription plans. Pharmacists, in turn, sign contracts so they will be included on a PBM’s approved list. Those contracts typically include the pharmacy’s agreement to face periodic audits.
Because of consolidation in the industry, declining to sign the contract is not much of an option, pharmacists say: In Mr. Adzema’s case, 70 percent of his commercial business comes from prescription plans managed by Express Scripts.
In Mr. Adzema’s audit, the single biggest deduction, $44,400, was for an anti-seizure drug that cost $3,200 to $3,700 per dose. He said the pharmacy had received phone authorization to fill two prescriptions for the drug that a 6-year-old Children’s Hospital patient needed.
As part of the audit, Express Scripts denied the claim, Mr. Adzema said, because his pharmacy records did not note who in the doctor’s office provided the authorization. The denial was also applied to each of the subsequent five refills for both scripts, 12 in all, for the $44,400 total.
Because Mr. Adzema has worked with the doctor’s office for many years — his father opened Adzema Pharmacy in 1959 — he believes he can get the documentation to recover nearly all of the $55,400 “but it’s taken days out of my life to do this,” he said.
“PBM’s are running roughshod over whoever they can. They can justify anything, even charging back $40,000 because the wrong initials are on the paperwork. They are obviously targeting big dollars and care nothing about the healthcare aspects of what they do.”
Read more >>