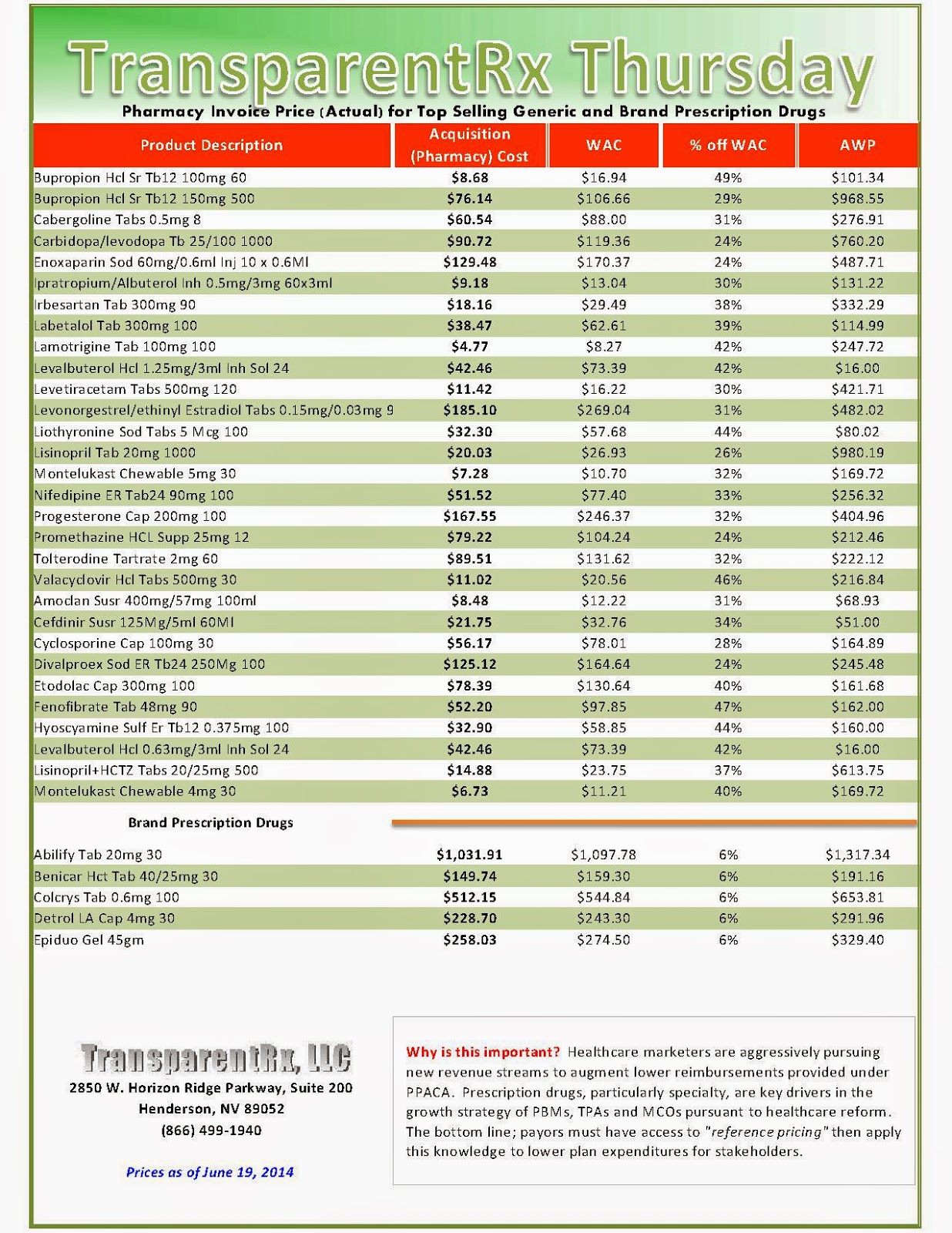
Reference Pricing: Pharmacy Invoice Cost (ACTUAL) for Top Selling Generic and Brand Prescription Drugs
The costs shared below are what our pharmacy actually pays; not AWP, MAC or WAC. The bottom line; payers must have access to “reference pricing.” Apply this knowledge to hold PBMs accountable and lower plan expenditures for stakeholders.
| How to Determine if Your Company [or Client] is Overpaying |
Step #2: In addition, request an electronic copy of all your prescription transactions (claims) for the billing cycle which coincides with the date of your price list.
Step #3: Compare approximately 10 to 20 prescription claims against the price list to confirm contract agreement. It’s impractical to verify all claims, but 10 is a sample size large enough to extract some good assumptions.
Step #4: Now take it one step further. Check what your organization has paid, for prescription drugs, against our pharmacy cost then determine if a problem exists. When there is a 5% or more price differential (paid versus actual cost) we consider this a problem.
When better pricing is discovered the contract language should stipulate the client be indemnified. Do not allow the PBM to limit the market check language to a similar size client, benefit design and/or drug utilization. In this case, the market check language is effectually meaningless.
Average Wholesale Price (AWP) for Twelve of the Most Expensive Specialty Drugs
- Hire a PBM willing to sign on as a fiduciary; transparent speak isn’t enough.
- Promote member use of manufacturer coupons for brand and specialty drugs. PBMs should communicate availability of all coupons to members.
- Pay only Cost Plus (no spreads or mark-ups) for all prescription drugs.
- Include a semi-annual market check in the contract language.
- Attain and exercise full auditing rights.
- Require the PBM to identify and pass along all sources of attributable revenue from manufacturers. Limiting agreements to ‘rebates’ leaves money on the table.
- Use Reference Pricing — different and much more effective (when applied) than an AWP reporting service.
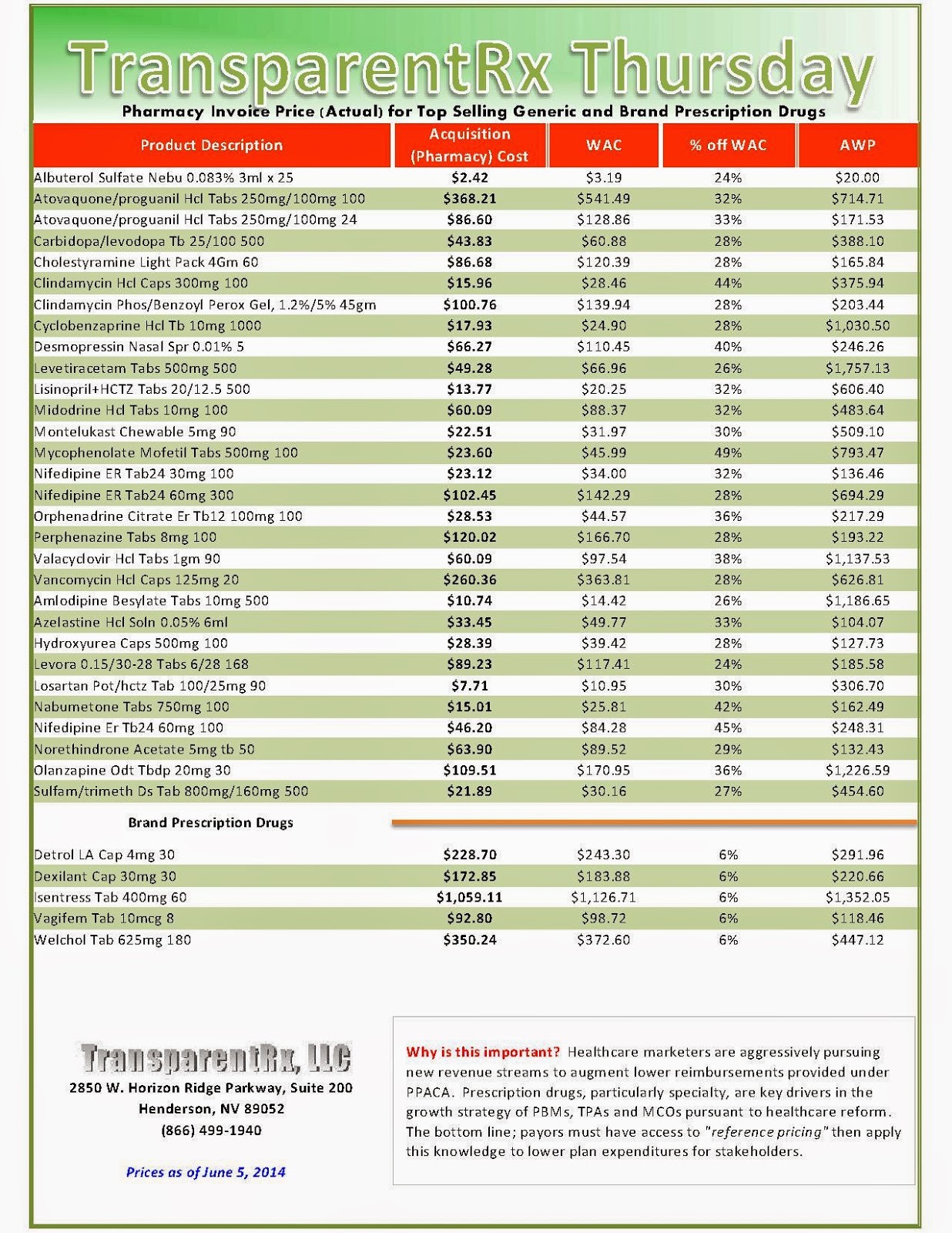
Reference Pricing: Pharmacy Invoice Cost (ACTUAL) for Top Selling Generic and Brand Prescription Drugs
The costs shared below are what our pharmacy actually pays; not AWP, MAC or WAC. The bottom line; payers must have access to “reference pricing.” Apply this knowledge to hold PBMs accountable and lower plan expenditures for stakeholders.
| How to Determine if Your Company [or Client] is Overpaying |
Step #2: In addition, request an electronic copy of all your prescription transactions (claims) for the billing cycle which coincides with the date of your price list.
Step #3: Compare approximately 10 to 20 prescription claims against the price list to confirm contract agreement. It’s impractical to verify all claims, but 10 is a sample size large enough to extract some good assumptions.
Step #4: Now take it one step further. Check what your organization has paid, for prescription drugs, against our pharmacy cost then determine if a problem exists. When there is a 5% or more price differential (paid versus actual cost) we consider this a problem.
When better pricing is discovered the contract language should stipulate the client be indemnified. Do not allow the PBM to limit the market check language to a similar size client, benefit design and/or drug utilization. In this case, the market check language is effectually meaningless.
Industry Consolidation Is Impacting PBM Customer Service
“Our large employer clients have been particularly interested in exploring the marketplace this year,” reports Josh Golden, a consultant at Pharmaceutical Strategies Group LLC. “This is driven by two primary factors: First, inconsistent service levels across the major PBMs have left a number of clients frustrated with their incumbent.
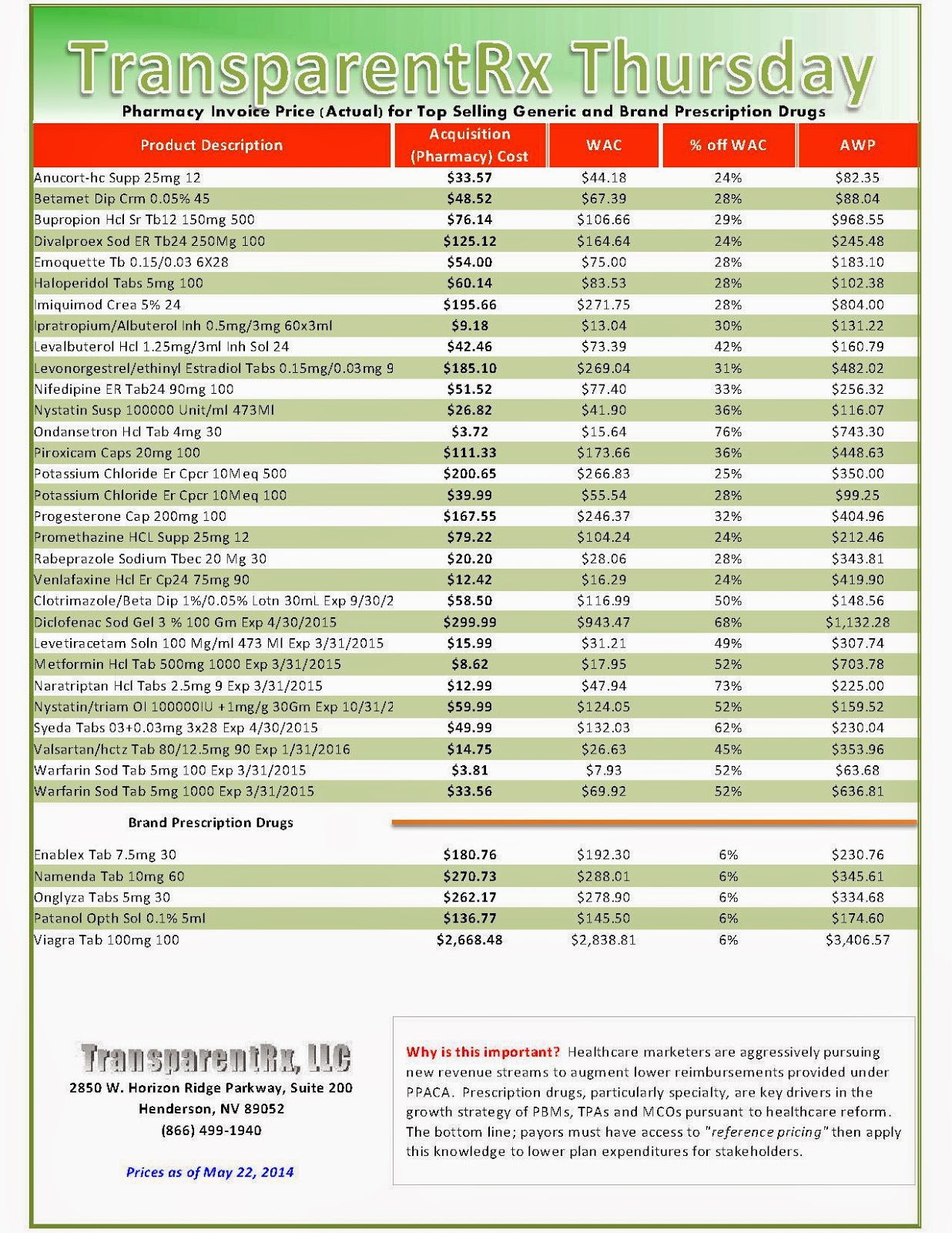
Reference Pricing: Pharmacy Invoice Cost (ACTUAL) for Top Selling Generic and Brand Prescription Drugs
The costs shared below are what our pharmacy actually pays; not AWP, MAC or WAC. The bottom line; payers must have access to “reference pricing.” Apply this knowledge to hold PBMs accountable and lower plan expenditures for stakeholders.
| How to Determine if Your Company [or Client] is Overpaying |
Step #2: In addition, request an electronic copy of all your prescription transactions (claims) for the billing cycle which coincides with the date of your price list.
Step #3: Compare approximately 10 to 20 prescription claims against the price list to confirm contract agreement. It’s impractical to verify all claims, but 10 is a sample size large enough to extract some good assumptions.
Step #4: Now take it one step further. Check what your organization has paid, for prescription drugs, against our pharmacy cost then determine if a problem exists. When there is a 5% or more price differential (paid versus actual cost) we consider this a problem.
When better pricing is discovered the contract language should stipulate the client be indemnified. Do not allow the PBM to limit the market check language to a similar size client, benefit design and/or drug utilization. In this case, the market check language is effectually meaningless.
The Insurance Industry is Picking a Fight with Pharmaceutical Companies Over the Rising Cost of Specialty Drugs
Drug makers say the high prices are necessary to recoup research and development costs. They also say insurers should cover more of the cost of pharmaceuticals.
 In the last week, AHIP CEO Karen Ignagni has launched a full-on public relations assault against drugmakers, who AHIP says threaten to threaten to bankrupt families and bust government healthcare budgets.
In the last week, AHIP CEO Karen Ignagni has launched a full-on public relations assault against drugmakers, who AHIP says threaten to threaten to bankrupt families and bust government healthcare budgets.Reference Pricing: Pharmacy Invoice Cost (ACTUAL) for Top Selling Generic and Brand Prescription Drugs
The costs shared below are what our pharmacy actually pays; not AWP, MAC or WAC. The bottom line; payers must have access to “reference pricing.” Apply this knowledge to hold PBMs accountable and lower plan expenditures for stakeholders.
| How to Determine if Your Company [or Client] is Overpaying |
Step #2: In addition, request an electronic copy of all your prescription transactions (claims) for the billing cycle which coincides with the date of your price list.
Step #3: Compare approximately 10 to 20 prescription claims against the price list to confirm contract agreement. It’s impractical to verify all claims, but 10 is a sample size large enough to extract some good assumptions.
Step #4: Now take it one step further. Check what your organization has paid, for prescription drugs, against our pharmacy cost then determine if a problem exists. When there is a 5% or more price differential (paid versus actual cost) we consider this a problem.
When better pricing is discovered the contract language should stipulate the client be indemnified. Do not allow the PBM to limit the market check language to a similar size client, benefit design and/or drug utilization. In this case, the market check language is effectually meaningless.
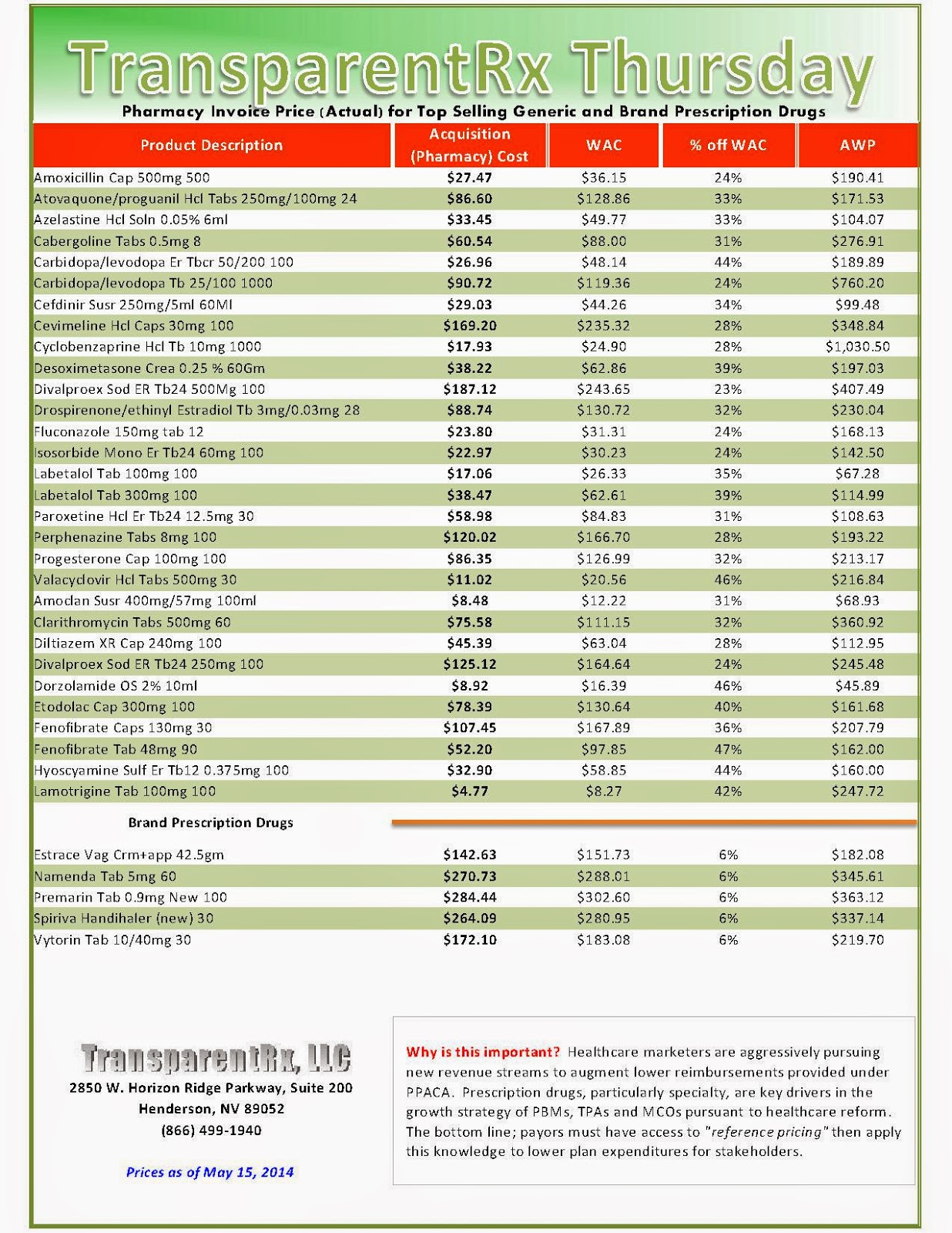
Reference Pricing: Pharmacy Invoice Cost (ACTUAL) for Top Selling Generic and Brand Prescription Drugs
The costs shared below are what our pharmacy actually pays; not AWP, MAC or WAC. The bottom line; payers must have access to “reference pricing.” Apply this knowledge to hold PBMs accountable and lower plan expenditures for stakeholders.
| How to Determine if Your Company [or Client] is Overpaying |
Step #2: In addition, request an electronic copy of all your prescription transactions (claims) for the billing cycle which coincides with the date of your price list.
Step #3: Compare approximately 10 to 20 prescription claims against the price list to confirm contract agreement. It’s impractical to verify all claims, but 10 is a sample size large enough to extract some good assumptions.
Step #4: Now take it one step further. Check what your organization has paid, for prescription drugs, against our pharmacy cost then determine if a problem exists. When there is a 5% or more price differential (paid versus actual cost) we consider this a problem.
When better pricing is discovered the contract language should stipulate the client be indemnified. Do not allow the PBM to limit the market check language to a similar size client, benefit design and/or drug utilization. In this case, the market check language is effectually meaningless.

_1.jpg)

_1.jpg)

_1.jpg)
_1.jpg)
_1.jpg)